Network tokenization
Network tokenization uses a payment network 's token provider to tokenize card information, allowing for payment transactions without the need to de-tokenize prior to processing. This token can be used for subsequent transactions related to the initial payment, including clearing, settlement, refunds, and dispute processing.
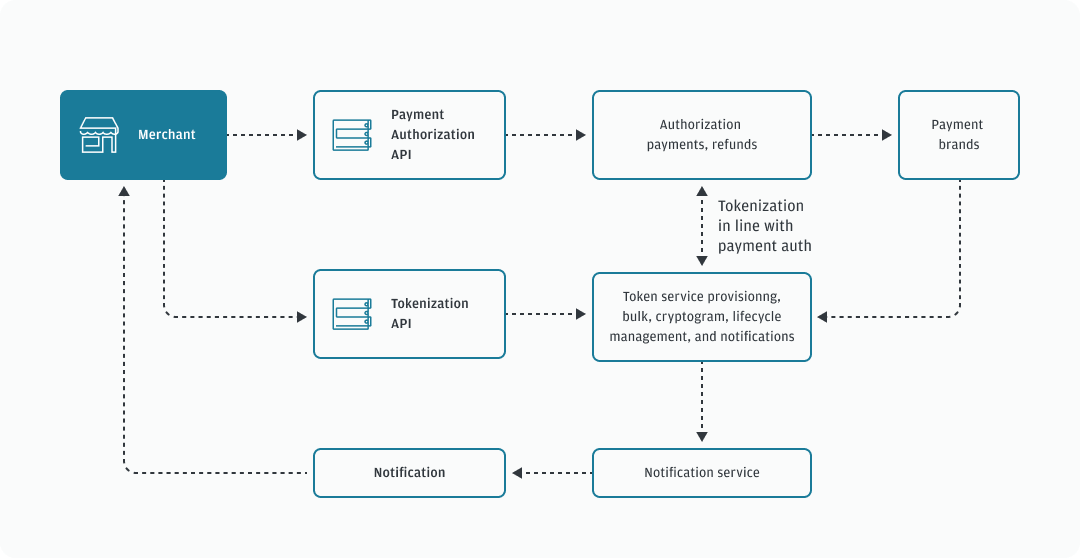
How network tokenization works
At a high-level, the tokenization process is comprised of the following steps:
- The consumer enters their payment card information into the merchant system.
- The merchant tokenizes the credentials using the Tokenization API.
- The merchant requests a cryptogram for the token.
- The token is used by the client to process a payment.
Before you begin
To set up and configure your network tokenization, you’ll need to obtain a token requestor identifier (TRID) from a payment network to generate requests for token provisioning using either one of these two methods:
- Request a TRID independently by connecting with the payment network.
- Contact your J.P. Morgan implementation specialist for help obtaining a TRID.
You can work with your J.P. Morgan implementation specialist to associate the provisioned TRIDs with a processing entity within our system.
Token provisioning
The token provisioning process secures sensitive payment information and validates your entity with your TRID. A network token with both of these values will be generated for an applicable card. Once activated, you can use this token as part of a payment transaction.
You have the option of generating tokens after a successful authorization, which reduces latency from consumer interactions.
Card token requirements
The following table lists the conditional and required fields for specific card networks for card tokenization:
| Payment brand | Required fields | Conditional fields |
|---|---|---|
| Visa |
|
|
| Mastercard |
|
|
| American Express |
|
Provide one of the following fields:
|
Tokenization approval status
The tokenizationApprovalStatus field displays the status of the network tokenization request. The values for this field include:
APPROVED— The tokenization decision was approved and the token is ready for processing.AUTH_REQUEST— The tokenization request was approved, but additional identity and verification (ID&V) processes are required to activate the token.DECLINED— The tokenization request was declined.
Once consumer authentication is complete, the tokenization response will contain the accountholderValidation object. This provides information about the method used for consumer validation. The available validationMethods are:
SMS
EMAIL
BANKING_APP
CUSTOMER_CARE
CALL_TO_USER
CUSTOMER_CARE_WEBSITE
Token cryptograms
Cryptograms are provided during payment authorization requests as proof of token validation. The following table highlights the transaction types that require cryptograms:
| Transaction type | Cryptogram required? |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| One-time cardholder initiated | Yes | A unique transaction that is initiated by the cardholder. |
| One-time client initiated (e.g., unscheduled transaction) | No | Transactions initiated by you, where the credentials are on file, but there is no predefined sequence for the transaction. |
| Installment transaction | No | A series of transactions that utilize stored credentials and represent an agreement where the cardholder permits you to initiate future transactions over a period for a single purchase. The initial transaction must carry a token cryptogram when initiated with a token. Subsequent actions do not require a cryptogram. |
| Split shipment | No | You receive an order for multiple items that are shipped separately, and each item is uniquely authorized. The initial transaction must carry a token cryptogram when initiated with a token. Subsequent actions do not require a cryptogram. |
Required data for cryptogram requests
The table below lists the required fields for specific card networks for cryptogram requests:
| API field | Visa | Mastercard | American Express |
|---|---|---|---|
| tokenCryptogramType |
|
Universal Cardholder Authentication Field (UCAF) | Dynamic card security code (DCSC) |
| randomNumber | N/A | Required | N/A |
| amount | N/A | N/A | Required |
| transactionType | Required | N/A | N/A |
| initiatedBy | Required | N/A | N/A |
| electronicCommerceIndicator | Required | Required | Required |
| tokenAuthenticationValue | Required | Required | Required |
Network tokenization with 3-D Secure
When using 3-D Secure (3DS) authentication with network token transactions, you must provide the electronic commerce indicator (ECI) and a token cryptogram as part of the payment authorization request. Depending on the 3DS version used, be sure to validate other conditional and/or required data elements necessary for payment in the 3-D Secure section.
Related
Request a token
Request a cryptogram
Manage token lifecycle
3-D Secure